A chiller plays a crucial role in controlling and maintaining the temperature of various processes involved in brewing beer. This cooling system helps regulate the temperature of liquids, equipment, and environments to ensure optimal conditions for the brewing process.
It primarily serves two main purposes:
1. Cooling Wort: One of the key stages in brewing beer is the boiling of wort. Wort is the liquid extracted from malted grains during the mashing process. After boiling, it needs to be rapidly cooled down to a specific temperature before yeast is added for fermentation. The chiller is used to lower the temperature of the hot wort quickly and efficiently. This rapid cooling helps preserve the delicate flavors and aromas of the beer and prevents unwanted chemical reactions that could negatively impact the final product.
2.Temperature Control During Fermentation: Yeast fermentation is a critical step in the brewing process. Yeast converts sugars in the wort into alcohol and carbon dioxide. Different types of beer require specific fermentation temperatures to achieve desired flavors, aromas, and other characteristics. The chiller is used to regulate the temperature of the fermentation vessels, ensuring that the yeast operates within the optimal temperature range. This control is important to maintain consistent and reproducible results across batches.
Chillers in brewery operations can come in various forms, including plate heat exchangers, immersion chillers, and glycol chillers. Glycol chillers are particularly popular in larger breweries, as they use a mixture of water and glycol to cool a glycol loop, which is then circulated through cooling jackets on fermentation vessels, brite tanks, and other equipment. This indirect cooling method allows precise temperature control without direct contact between the cooling fluid and the beer, preventing contamination. (We talk more about monitoring incoming and outgoing glycol temperatures in this blog.)
Why Worry About the Wort?
It’s a pretty big deal and gets each batch off to brew its best life. The wort production process is one of the most critical and foundational steps in brewing beer. It sets the stage for the entire brewing process and significantly influences the final flavor, aroma, color, mouthfeel, and overall quality of the beer.
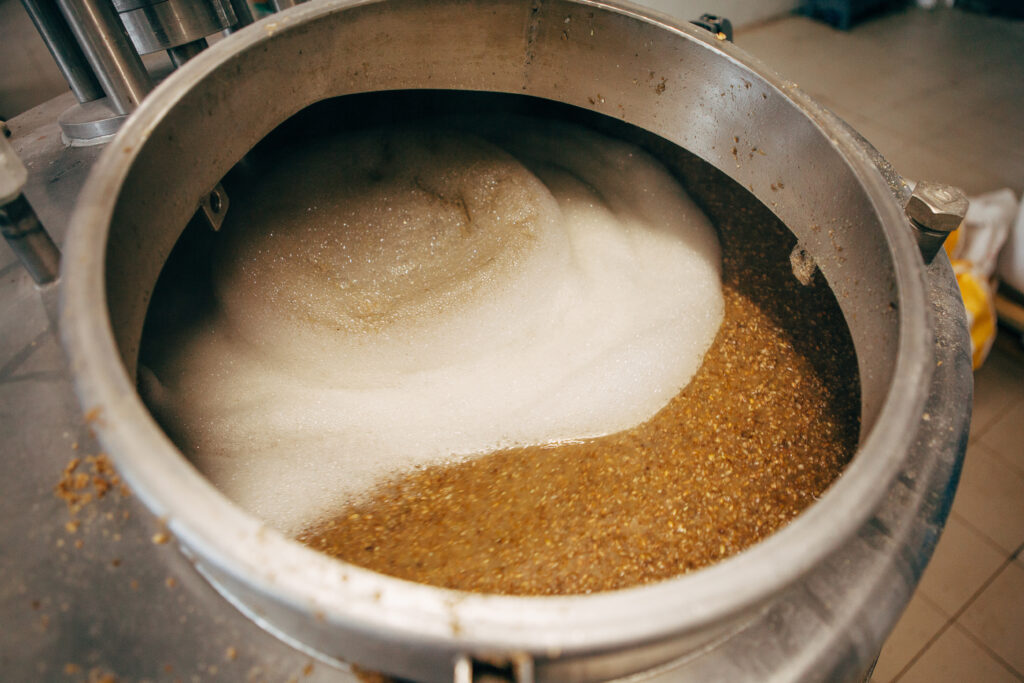

Let’s break it down further:
Extraction of Fermentable Sugars: During the wort production process, malted grains are mashed with hot water to extract fermentable sugars, proteins, enzymes, and other compounds. These sugars serve as the primary food source for yeast during fermentation,
where they are converted into alcohol and carbon dioxide. The types and amounts of sugars extracted during mashing directly impact the beer’s alcohol content, sweetness, and body.
Flavor and Color Development: The temperature and duration of the mashing process influence the types of sugars and other molecules extracted from the malt. This, in turn, affects the beer’s flavor, color, and mouthfeel. Mashing at different temperatures can produce varying levels of sweetness, body, and malt character. The variety of malt and its roasting level also contribute to color and flavor development.
Enzyme Activation: Mashing activates enzymes present in the malt, such as amylase, which break down complex starches into simpler sugars that yeast can ferment. Controlling the mash temperature allows brewers to control the balance between different types of sugars, affecting the beer’s sweetness and dryness.
Protein Modification: Mashing also leads to the modification of proteins in the malt, which affects the beer’s foam stability and overall mouthfeel. Proper protein modification helps create a stable and desirable foam head on the beer.
Prevention of Undesirable Compounds: The wort process involves boiling the extracted liquid to sterilize it and extract bitterness from hops. Boiling also helps drive off unwanted volatile compounds, such as dimethyl sulfide (DMS), which can contribute off-flavors to the beer.
Hops Utilization: Hops are typically added during the boil to provide bitterness, flavor, and aroma to the beer. The timing of hop additions during the boil influences these characteristics. The wort’s pH and gravity also affect how hops interact with the beer.
Sanitation and Sterilization: The wort production process involves boiling, which sanitizes the liquid and prevents the growth of unwanted microorganisms. This step is crucial to prevent contamination that could lead to off-flavors or spoiled beer.
Yeast Health and Fermentation: The quality and composition of the wort directly impact the health of the yeast during fermentation. A well-balanced wort provides the necessary nutrients for yeast growth and fermentation activity, leading to consistent and desirable fermentation outcomes.
As stated, the wort phase in production lays the foundation for the entire beer-making process. The decisions made during mashing, boiling, and hop additions significantly impact the beer’s flavor, aroma, color, body, and overall quality. Brewmasters and brewers carefully control these steps to create wort that meets the specific characteristics of the desired beer style, setting the stage for successful fermentation and a high-quality final product. Which bring us to what could go wrong …
Chiller Malfunctions
If a chiller malfunctions in a brewery operation, it can lead to a range of issues that can negatively impact the quality of the beer being produced and potentially disrupt the entire brewing process.
These potential chiller problems include:
Temperature Fluctuations: A malfunctioning chiller might not be able to maintain stable temperatures in the brewing process. This can result in temperature fluctuations during wort cooling or fermentation, leading to inconsistent flavors, aromas, and overall beer quality. Incorrect temperatures can also affect yeast activity and fermentation kinetics, potentially leading to off-flavors and unwanted byproducts.
Extended Cooling Times: Inefficient cooling due to a malfunctioning chiller can extend the time it takes to cool down the wort after boiling. Prolonged cooling times can increase the risk of bacterial contamination, as the wort is exposed to the environment for a longer period. This can result in sour or off-flavored beer.
Yeast Health and Fermentation Issues: Yeast is highly temperature-sensitive, and improper fermentation temperatures caused by a malfunctioning chiller can stress or inhibit yeast activity. This can lead to incomplete fermentation, inconsistent alcohol content, and undesirable flavors in the final product. Yeast health is crucial for achieving the desired beer characteristics.
Inconsistent Batches: Breweries strive for consistency in their beer production. A malfunctioning chiller can lead to batch-to-batch variability, making it challenging to replicate the same flavor profiles and quality across different batches of beer. Inconsistencies can damage a brewery’s reputation and customer loyalty.
Quality Compromises: Incorrect temperatures and extended exposure to non-sterile conditions can increase the risk of contamination by unwanted microorganisms. This can result in the growth of off-flavor-producing bacteria or wild yeast strains, causing beer to have undesirable tastes and aromas that deviate from the intended flavor profile.
Production Delays: Chiller malfunctions can lead to production delays, as the brewing process may need to be halted or modified to address the cooling issues. This can disrupt the brewery’s production schedule and impact its ability to meet customer demand.
Waste and Financial Losses: Inefficient cooling processes may lead to higher energy consumption, increased water usage, and wastage of raw materials. Additionally, if batches of beer need to be discarded due to quality issues arising from chiller malfunctions, it can result in financial losses for the brewery.
Equipment Damage: Malfunctions can also cause stress on the chiller equipment itself, potentially leading to more severe mechanical failures. These failures can result in longer downtime, costly repairs, and replacement of equipment.
There are so many intertwined variables that can throw off a brew—some are subtle and more suspectable to temperature fluctuates than others. To prevent these potential problems, breweries invest in regular chiller maintenance, monitoring systems, and backup cooling solutions. Maintaining the reliability and performance of chillers is crucial for consistent beer quality, efficient production processes, and overall brewery success.
Safeguarding Against Chiller Failure
Your first and last line of defense is to go on the offense and establish real-time chiller monitoring.
Choose the Right Monitoring System: Select a chiller monitoring system that offers real-time data, remote access, and customizable alerts to keep you informed about your chiller’s performance.
Train Your Staff: Ensure that your brewery staff is trained to understand the importance of chiller monitoring and how to interpret the data provided by the monitoring system.
Establish a Maintenance Schedule: Use the data gathered from your real-time monitoring system to develop a proactive maintenance schedule, helping to extend the life of your chiller and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Check Out BrewOps Chill
BrewOps offers a fast and easy-to-install solution: the BrewOps Chill, a real-time chiller monitoring solution. With BrewOps Chill you can trend your incoming and outgoing glycol temperatures in real-time, from anywhere in the world. With a non-invasive clamp-on design, the BrewOps Chill installs onto any metal-walled pipe in seconds. With advanced thermal isolation and algorithms, the BrewOps Chill measures temperature with an industry leading .2°F accuracy. By monitoring the temperature differential of your chillers’ glycol lines, breweries can prevent catastrophic loss of product due to unexpected failures, while maintaining optimal brewing conditions, by dialing in the performance of their chiller to meet their specific cellar needs. By implementing this proactive monitoring system and signing up for remote alerts and trends, you’ll be taking a proactive approach to chiller maintenance—and most importantly— safeguard your tasty brews.
What you gain:
- 24/7 incoming and outgoing glycol monitoring
- Reduction in unexpected outages with real-time notifications
- Peace of mind when you are away from the brewery
- Financial security—a simple solution to mitigate risks
Implement real-time chiller monitoring solutions, designed with your needs in mind:
- Real-time noninvasive pipe-temperature monitoring
- Fast, easy installation, no wiring required
- Remotely view alerts, trends, and chiller performance using the BrewOps app
- Rugged, industrial construction, outdoor UV-rated
- Replaceable long-lasting battery
- Designed with brewers, for brewers
Start monitoring your chiller today and realize the benefits of a more efficient, cost effective, and reliable brewing operation.
Cheers!